1. What is diode?
2. Type of diode?
There are several types of diodes are available for use in electronics design,

The Zener diode is used to provide a stable reference voltage. As a result, it is used in vast amounts. It works under reverse bias condition and found that when a particular voltage is reached it breaks down. If the flow of current is limited by a resistor, it activates a stable voltage to be generated. This type of diode is widely used to offer a reference voltage power supplies

A diode is a specialized electronic component with two electrodes called the anode and the cathode. Most diodes are made with semiconductor materials such as silicon, germanium, or selenium.
There are several types of diodes are available for use in electronics design,
Backward Diode
2.1This type of diode is also called the back diode, and it is not widely used. The backward diode is a PN-junction diode that is similar to the tunnel diode in its process. It finds a few special applications where its specific properties can be used.
2.2BARITT Diode
The short term of this diode Barrier Injection Transit Time diode is BARITT diode. It is applicable in microwave applications and allows many comparisons to the more widely used IMPATT diode
2.3Laser Diode
The laser diode is not the similar as the ordinary LED (light emitting diode) because it generates coherent light. These diodes are extensively used in many applications like DVDs, CD drives and laser light pointers for PPTs. Although these diodes are inexpensive than other types of laser generator, they are much more expensive than LEDs. They also have a partial life
2.4Light Emitting Diode
The term LED stands for light emitting diode, is one of the most standard types of the diode. When the diode is connected in forwarding bias, then the current flows through the junction and generates the light. There are also many new LED developments are changing they are LEDs and OLEDs
2.5Photodiode
The photodiode is used to detect light. It is found that when light strikes a PN-junction it can create electrons and holes. Typically, photodiodes operate under reverse bias condition where even a small amount of flow of current resulting from the light can be simply noticed. These diodes can also be used to produce electricity
2.6Schottky Diode
The Schottky diode has a lower forward voltage drop than ordinary Si PN-junction diodes. At low currents, the voltage drop may be between 0.15 & 0.4 volts as opposed to 0.6 volts for a Si diode. To attain this performance they are designed in a different way to compare with normal diodes having a metal to semiconductor contact. These diodes are extensively used in rectifier application, clamping diodes, and also in RF applications

2.7Zener Diode
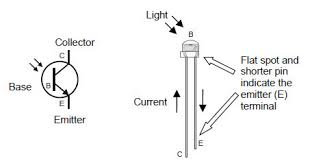
3. Diode test and identify?
Test a Diode using a Digital Multimeter
Meter with a “Diode check” function displays the forward voltage drop of 0.548 volts instead of a low resistance.
Ohmmeter Mode Testing Procedure
4. Application of diode?
Radio demodulation :
The first use for the diode was the demodulation of amplitude modulated (AM)
radio broadcasts. The history of this discovery is treated in depth in
the radio article. In summary, an AM signal consists of alternating positive and
negative peaks of voltage, whose amplitude or “envelope” is proportional to the
original audio signal, but whose average value is zero. The diode (originally a
crystal diode) rectifies the AM signal, leaving a signal whose average amplitude is
the desired audio signal. The average value is extracted using a simple filter and
fed into an audio transducer, which generates sound.
Power conversion: Rectifiers are constructed from diodes, where they are used to convert alternating
current (AC) electricity into direct current (DC). Automotive alternators are a
common example, where the diode provides better performance than the
commutator of earlier dynamo.
Similarly, diodes are also used in Cockcroft–Walton voltage multipliers to
convert AC into higher DC voltages.
Over-voltage protection :Diodes are frequently used to conduct damaging high voltages away from sensitive
electronic devices. They are usually reverse-biased (non-conducting) under normal
circumstances. When the voltage rises above the normal range, the diodes become
forward-biased (conducting). For example, diodes are used in ( stepper motor and
H-bridge ) motor controller and relay circuits to de-energize coils rapidly without
the damaging voltage spikes that would otherwise occur. (Any diode used in such
an application is called a flyback diode). Many integrated circuits also incorporate
diodes on the connection pins to prevent external voltages from damaging their
sensitive transistors. Specialized diodes are used to protect from over-voltages at
higher power
Logic gates: Diodes can be combined with other components to construct AND and OR logic
gates. This is referred to as diode logic.
Ionising radiation detectors :In addition to light, mentioned above, semiconductor diodes are sensitive to more
energetic radiation. In electronics, cosmic rays and other sources of ionising
radiation cause noise pulses and single and multiple bit errors. This effect is
sometimes exploited by particle detectors to detect radiation. A single particle of
radiation, with thousands or millions of electron volts of energy, generates many
charge carrier pairs, as its energy is deposited in the semiconductor material. If the
depletion layer is large enough to catch the whole shower or to stop a heavy
particle, a fairly accurate measurement of the particle’s energy can be made,
simply by measuring the charge conducted and without the complexity of a
magnetic spectrometer or etc. These semiconductor radiation detectors need
efficient and uniform charge collection and low leakage current. They are often
cooled by liquid nitrogen. For longer range (about a centimetre) particles they need
a very large depletion depth and large area. For short range particles, they need any
contact or un-depleted semiconductor on at least one surface to be very thin. The
back-bias voltages are near breakdown (around a thousand volts per centimetre).
Germanium and silicon are common materials. Some of these detectors sense
position as well as energy. They have a finite life, especially when detecting heavy
particles, because of radiation damage.
Silicon and germanium are quite different in their ability to convert gamma rays to
electron showers.
Semiconductor detectors for high energy particles are used in large numbers.
Because of energy loss fluctuations, accurate measurement of the energy deposited
is of less use.
Temperature measuring: A diode can be used as a temperature measuring device, since the forward voltage
drop across the diode depends on temperature. From the Shockley ideal diode
equation given above, it appears the voltage has a positive temperature coefficient
(at a constant current)but depends on doping concentration and operating
temperature. The temperature coefficient can be negative as in typical thermistors
or positive for temperature sense diodes down to about 20 degrees Kelvin.
Current steering :Diodes will prevent currents from flowing in unintended directions. To supply
power to an electrical circuit during a power failure, the circuit can draw current
from a battery. An Uninterruptible power supply built in this may use diodes to
ensure that current is only drawn from the battery when necessary.
Similarly, small boats typically have two circuits each with their own
battery/batteries: one used for engine starting; one used for domestics. Normally
both are charged from a single alternator, and a heavy duty split charge diode is
used to prevent the higher charge battery (typically the engine battery) from
discharging through the lower charged battery when the alternator is not running.
pdf free downlode









No comments